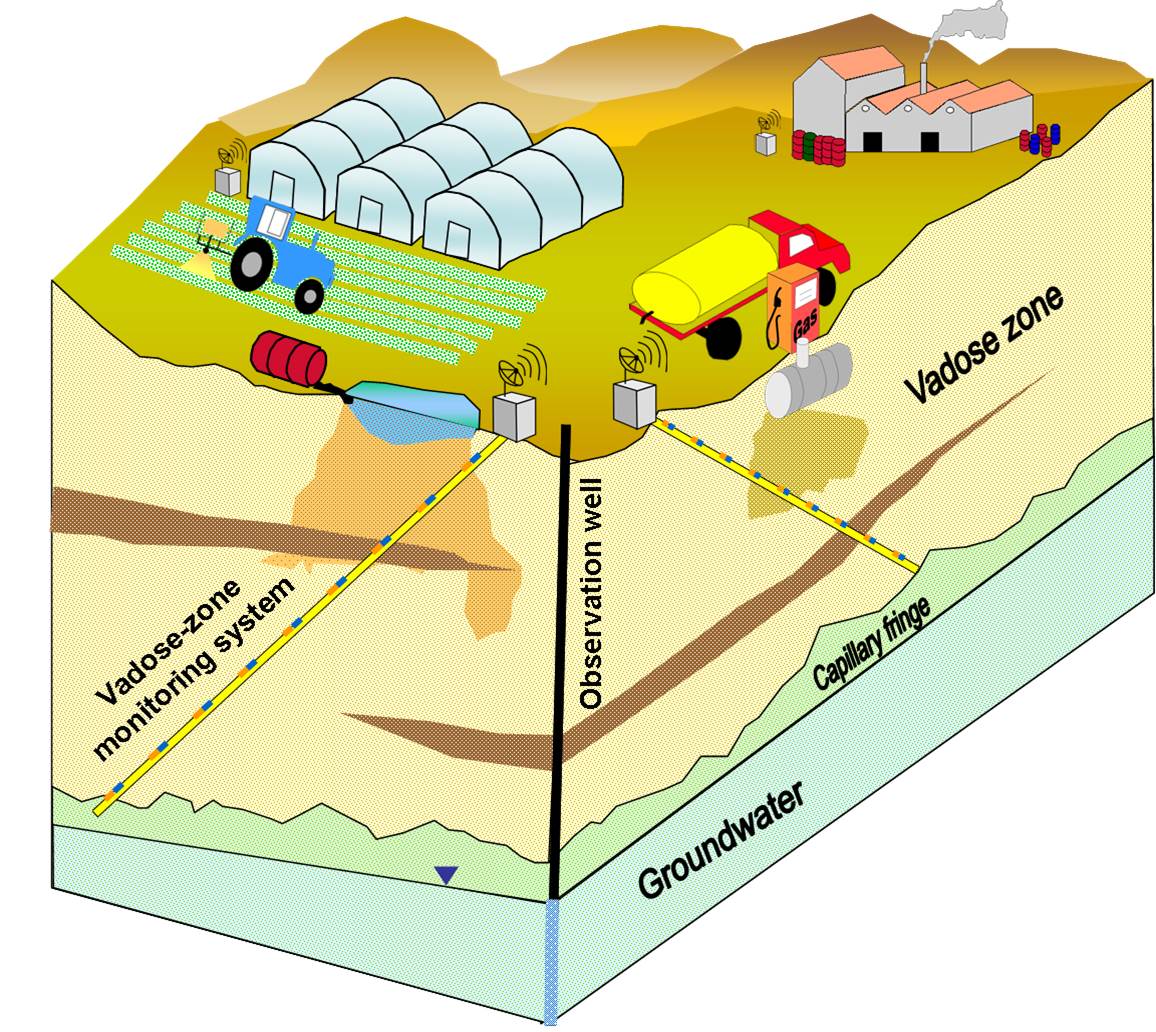
Minimization subsurface pollution depends on reliable and effective monitoring programs. Today, most groundwater monitoring programs are based on observation wells. Consequently, identification of pollutants in groundwater is clear evidence that contaminants already crossed the entire vadose-zone and accumulated in the aquifer. Unfortunately, only little can be done to fully remediate contaminated aquifers. Therefore effective monitoring program that aims at protecting groundwater from pollution must include vadose-zone monitoring technologies. Sensoil monitoring technology provide "early warning" on contamination processes in the vadose zone long before aquifer contamination turns evident.
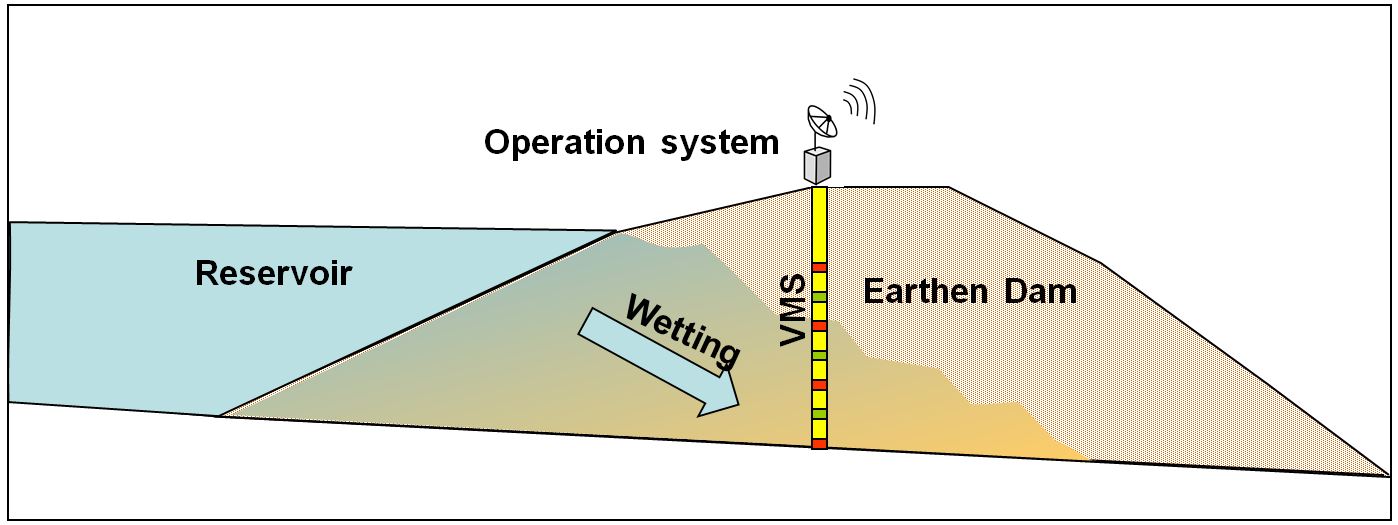
Water infiltration through earthen dams may weaken its stability and potentially lead to dam breach. Today most monitoring programs in earthen dams are bases on measurement of the phreatic level in piezometers. Nevertheless detection of free water in well indicates undesired saturation of the dam sediment. Application of Sensoil monitoring technology in earthen dams provides Real time continuous information on the dam sediment moisture. Detailed analysis moisture data obtained by the VMS across the dam is used to provide early warning on potential weakening of the dam stability.
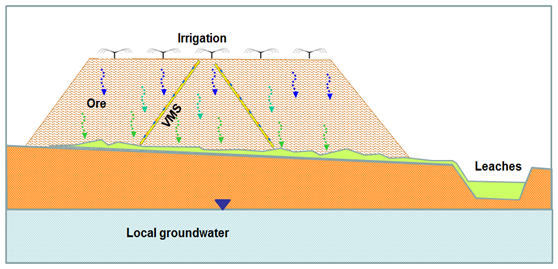
Heap leaching mining typically involve leaching of crushed ore with diluted acid solution, using irrigation system such as sprinklers or drippers. Upon percolation of the leaching solvent in the ore heap metal oxides dissolve and drain down to the bottom of the heap. As a result the drained solution is enriched with the desired metal which is than processes from the metal bearing solution. Water percolation through the ore heap take place in unsaturated condition and derived by gravity and capillary forces. Implementation of Sensoil monitoring technology in active heap leach pad provides the pad managers with real time information the leaching efficiency. Data collected by the VMS allows direct measurements of the water flow velocities and measure the chemical evolution of the percolating solvent in the unsaturated ore. As result the solvent application cycles may be managed according to the actual chemical evolution of the percolating water in the heap in order to increase mineral extraction efficiency.